 |
 |
| Water spinach and Enydra fluctuans used to treat animal wastewater; effects on COD values | Growth rates of rabbits fed water spinach or Enydra fluctuans alone or mixed 50:50 with Para grass |
|
MEKARN Conference 2010 |
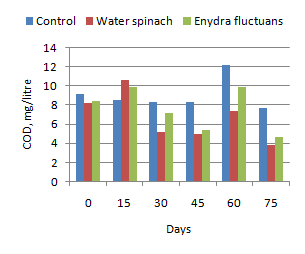
Experiment 1 evaluated the role of water spinach and Enydra fluctuans in treating animal wastewater by measurements of pH, DO and COD of wastewater at different time points of 0, 15, 30, 45, 60 and 75 days after the plants were applied and also to analyze chemical contents and biomass yield of the plants at 50 and 80 days of planting. Water spinach and Enydra fluctuans can be used to treat animal wastewater. The biomass yields of Water spinach and Enydra fluctuans after two harvests were 7.95 and 17.6 tonnes/ha, respectively. The two plants are of similar nutritive value (20.3 – 21.1% CP in DM)
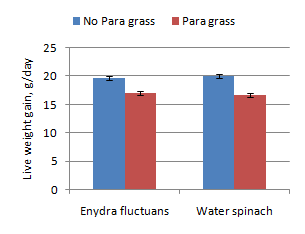
In experiment 2, forty-six crossbred rabbits (local x improved breed) at 6-7 weeks of age, were arranged in a Complete Randomized Design with 4 treatments and 3 replications to determine the effect of Enydra fluctuans and water spinach on growth performance of crossbred rabbits . The experiment lasted for 60 days. There were no differences between Enydra fluctuans and water spinach in dry matter intakes (DMI) daily weight gain (DWG) and feed conversion ratio (FCR) on the rabbits. Both were better given as sole feeds than offered with 50:50 ratio (DM basis) with Para grass.
 |
 |
| Water spinach and Enydra fluctuans used to treat animal wastewater; effects on COD values | Growth rates of rabbits fed water spinach or Enydra fluctuans alone or mixed 50:50 with Para grass |