 |
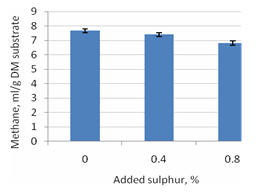 |
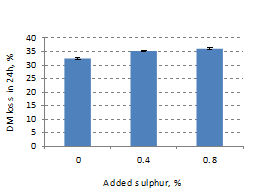
| Figure 1. DM loss as % of substrate | Figure 2. Methane production |
|
MEKARN Conference 2010 |
Three treatments: SN (Sodium nitrate), SN-0.4S (Sodium nitrate + 0.4 % Sulphur addded to diet) and SN-0.8S (Sodium nitrate + 0.8 % Sulphur) were compared in an in vitro experiment with 3 repetitions in a completely randomized design, using as substrate, a basal diet of NaOH-treated rice straw and cottonseed meal. The forage components of the diets were dried and milled through a 1 mm screen and mixed with the other components of the diet. Representative samples (20 g DM) were put in an incubation flask (2500ml) to which were added 1.6 liters of buffer solution and 400ml of rumen fluid, prior to filling each flask with carbon dioxide. The rumen fluid for each treatment was obtained from the rumen-fistulated cattle that were on the same dietary treatments. The flasks were then incubated at 38 0 C in a water bath for 72h. During the incubation, each flask was connected to an aluminium bag for total collection of gas over the 72h incubation. At the end of the incubation the total gas volume was recorded and samples analyzed for the proportions of methane and carbon dioxide. The same treatments and the same methods were done to measure digestibility. Representative samples (0.5 g DM) were put in flasks (100ml). The flasks were then incubated at 38 0 C in a water bath for 24h to measure DM losses.
The methane:carbon dioxide ratios did not among treatments of experiment (P= 0.18). However, DM loss (%) (Figure 1) and CH4 production (ml CH4/g DM substrate) (Figure 2) differed at P = 0.027 and P = 0.006 respectively, with increase in DM loss and decrease in methane with increase in the supplement of sulphur.
Key words: Sodium nitrate, cotton seed meal, in vitro, sodium nitrate, sulphur
 |
 |
| Figure 1. DM loss as % of substrate | Figure 2. Methane production |