Effect of different protein levels derived from mixtures of water spinach
and fresh sweet potato vines in basal diets of broken rice or cassava root meal
and rice bran for growing pigs
Thim Sokha, T R Preston* and Khieu Borin**
Royal University of Agriculture, Faculty of Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine
Sokha_rua@yahoo.com
* TOSOLY-UTA, AA #48, Socorro, Santander, Colombia
**CelAgrid, Phnom Penh, Cambodia
Abstract
Thirty two crossbred pigs (mean initial weight 11.33 kg) were housed in individual pens and allocated to 8 treatments according to a 2*4 factorial arrangement. The factors were two sources of energy: broken rice compared with cassava root meal mixed with rice bran; and four levels of crude protein (10, 12, 14 and 16% in dry matter (DM)). The source of supplementary crude protein was a mixture (50:50 as DM) of water spinach with sweet potato vines. The duration of the experiment was 150 days, from July 02 to December 02, 2006.
There were curvilinear relationships between dietary crude protein concentration and live weight gain and feed conversion with the optimum point at 14% crude protein in the diet DM. Growth rates were the same but feed conversion was better when the energy source was broken rice rather than cassava root meal and rice bean. Growth rates and feed conversion improved with time on the experiment.
Key words: Curvilinear, feed conversion, response curves,
Introduction
Pig production plays an important role as a major source of income of the rural poor farmers; moreover it also provides manure as the fertilizer for cropping. In Cambodia, 75% of the total pig producers are farmers who live in the remote areas (Khieu Borin et al 1996). As the human population grows, there will be a need for more food to meet the increasing demand. The production of meat from non-ruminants (pigs and poultry) is increasing faster than from the ruminants because of the quick turnover of the capital and the ease of access to the market. However, the traditional feeds for pigs are cereal grains and soya bean which are also eaten by people. Therefore it is important to develop pig feeding systems which are non-competitive with humans. The most common non-conventional feeds which are used for pigs in the country are rice bran, banana stems, sweet potato vine, water spinach, water hyacinth, duckweed, cassava and dried fresh water fish.
Water spinach (Ipomoea aquatica) is traditionally used in Cambodia as a vegetable for both humans and animals. It has a short growth period and is resistant to common insect pests and diseases; it can also be cultivated either in dry or flooded soils. It responds dramatically to fertilization with effluent from biodigesters charged with pig manure (Kean Sopea and Preston 2001). The yield was up to 24 tonnes/ha of fresh biomass achieved in a growth period of 30 days. The leaves and stems of water spinach contain more than 20 % crude protein in dry matter basis (Le Thi Men et al 1999; Le Thi Men et al 2000; Kean Sopea et al 2001; Göhl 1981; Ly et al 2002). Water spinach has been used successfully to replace part of the protein in a diet of sugar cane juice for breeding sows (Le Thi Men and Bui Hong Van 1993). Prak Kea et al (2003) reported that there was a linear increase in growth rates in pigs fed water spinach, palm oil and broken rice when up to 6% fish meal (in diet DM) replaced equivalent amounts of water spinach, which they attributed to an improved amino acid balance, especially in terms of the sulphur-rich amino acids. Chhay Ty and Preston (2006a) reported that water spinach was more palatable and had higher digestibility than cassava leaves.
Sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas L. (Lam)) is the third most common crop in Cambodia after rice and maize and is a valuable pig feed. The roots provide energy and the leaves provide protein, and both can be used fresh, dried or fermented into silage (Woolfe 1992). It is a common feed for pigs and also has high biomass yields of both tubers and vines (Le Van An et al 2003). Traditionally, sweet potato is used as human food; however at present it is also used as feed for farm livestock, especially pigs. The biomass yield of sweet potato is high and can reach up to 50 tonnes of foliage and 30 tonnes of roots/ha/year according to Hoang Vu Tuyen et al (1993). Sweet potato vines can be harvested several times throughout the year (Dahniya 1981; Le Van An et al 2003).
Sweet potato leaves are reported to have a crude protein content of 25.5 – 29.8 % in DM, which is almost double the level in the stems (10 to 14% in DM) (Woolfe 1992; Ishida et al 2000). The leaves can be used fresh, dried or as silage, and can replace fish meal and groundnut cake as a protein source for growing pigs (Le Van An 2004). Growing pigs fed sweet potato leaves with addition of synthetic lysine had daily live-weight gains of 536 g per day, which was similar to that of pigs fed a control diet with fish meal as the protein source (542 g/day) (Le Van An 2004). Le Thi Men et al (2000) and Duyet Hoang Nghia et al (2003), Duyet Hoang Nghia et al (2004) reported that the most suitable proportion of sweet potato leaves in the diet of sows is from 30 to 40 % (in DM) in pregnancy, and 20 to 30 % in lactation.
Rice bran is one of the main by-products used in pig raising (Rozemuller 1998). However, the rice-bran produced by traditional mills in Cambodia is of low energy density. Broken rice is another by-product of rice milling but with the advantage of a high energy density as it is almost free of fibre. Cassava root meal is another energy source available in Cambodia. However, it is low in protein. According to Eusebio (1980), the inclusion of more than 50% cassava root meal in the ration decreases the live weight gain and the feed conversion of pigs.
The
aim of the presented study was to determine the effect of different levels of
crude protein, derived from combinations of sweet potato vines and water spinach
in diets, on intake, growth rate and feed conversion by crossbred pigs fed basal
diets based on broken rice or cassava root meal mixed with rice bran.
Material and methods
Location and duration
The experiment was conducted at the ecological farm of the Center for Livestock and Agriculture Development (CelAgrid) located in Preah Theat village, Rolous commune, Kandal Steung district, Kandal province, about 25 km from South of Phnom Penh city, Cambodia. The average annual temperature in this location is from 26 to 31 0C. The experiment was started on 02 July and finished on 02 December 2006.
Experimental design
Thirty two crossbred pigs (Local*Yorkshire or Local*Landrace) were used in the experiment which was carried out as a 2*4 factorial arrangement. There were 4 replicates arranged as 4 blocks; 2 blocks had 16 castrate male pigs with average initial live weight of 11.7 kg and 2 blocks had 16 females with average initial live weight of 11.0 kg. The factors were four protein levels (10, 12, 14 and 16% in DM) and two energy sources (Broken rice alone or rice bran mixed with cassava root meal).
Energy source: Cassava root meal plus rice bran (CRM-RB) or broken rice (BR)
Level of crude protein: 10 ,12, 14 and 16 % in DM
Animals and management
The pigs were housed in individual pens with concrete floors and were provided with drinking nipples. All the pigs were vaccinated against hog cholera, pasteurellosis and salmonellosis diseases. They were also treated with an anti-parasitic drug (Ivomic given by injection) once after the vaccination.
Housing, feeding and management
Broken rice and rice bran were purchased from a local rice mill. The cassava root meal was purchased from the local market. Sweet potato vines were harvested initially from plots in CelAgrid (Photo 1). However, because of flooding in the Centre, it was later purchased from farmers in Kandal and Takeo provinces. The water spinach was bought from traders who harvested it from lagoons receiving waste water from Phnom Penh city (Photo 2).
|
|
|
|
|
The water spinach and sweet potato vines were chopped into 1-2 cm lengths and mixed in the ratio of 50:50 (DM basis). The forages were given as the first feed at 07.00h. The energy component was given at 12.00 and 16.00 h.
Measurements and data collection
The pigs were weighed in the morning before feeding, at the start of the experiment and then every 10 days. Individual daily weight gain was calculated by the regression of live weight on time in days. Individual feed intake was calculated from weight of fresh material offered minus the residue collected the next morning. Feed offered and feed refusals were recorded daily. Feed conversion ratio was calculated from individual daily DM intake and live weight gain. Samples of feeds offered and refusals were analysed for DM by microwave radiation (Undersander et al 1993) and N following the methods of AOAC (1990).
Statistical analysis
The
data were analysed statistically using the General Linear Model (GLM) option of
Minitab (version 13.31) ANOVA software Minitab (2000). Sources of variation
were: protein level, energy source, interaction between foliage* energy source,
blocks and error.
Results
Feed intake
The composition of the dietary ingredients is shown in Table 1.
|
Table 1. Composition of the ingredients in the diets |
||
|
|
% DM |
% Crude protein in DM |
|
Broken rice |
86.0 |
9.43 |
|
Rice bran |
91.3 |
12.3 |
|
Cassava root meal |
88.4 |
3.18 |
|
Water spinach |
8.90 |
28.7 |
|
Sweet potato vine |
16.0 |
16.6 |
DM intakes of the forages were higher on the CRM-RB diet than on the BR diet (Table 2) at all stages of the experiment.
|
Table 2. Mean values for DM intake of pigs fed basal diets of broken rice (BR) or cassava root meal plus rice bran ( CRM-RB) |
||||
|
|
BR |
CRM-RB |
SEM |
Prob |
|
DM intake, g/day ( 0-50 days) |
||||
|
WS-SPV |
106 |
120 |
2.41 |
0.001 |
|
BR |
294 |
0 |
2.41 |
0.001 |
|
CRM-RB |
0 |
320 |
2.40 |
0.001 |
|
Total |
400 |
440 |
4.70 |
0.001 |
|
CP |
45.7 |
53.9 |
0.77 |
0.001 |
|
g/kg.LW |
34.6 |
35.3 |
0.25 |
0.043 |
|
DM intake, g/day ( 50-100 days) |
||||
|
WS-SPV |
144 |
185 |
2.16 |
0.001 |
|
BR |
386 |
0 |
2.09 |
0.001 |
|
CRM-RB |
0 |
410 |
2.30 |
0.001 |
|
Total |
530 |
595 |
4.56 |
0.001 |
|
CP |
66.9 |
77.8 |
0.65 |
0.001 |
|
g/kg.bw |
31.2 |
34.2 |
0.17 |
0.001 |
|
DM intake, g/day ( 100-150 days) |
||||
|
WS-SPV |
143 |
212 |
3.31 |
0.001 |
|
BR |
554 |
0 |
5.34 |
0.001 |
|
CRM-RB |
0 |
635 |
3.60 |
0.001 |
|
Total |
697 |
847 |
8.88 |
0.001 |
|
CP |
84.7 |
108 |
1.33 |
0.001 |
|
g/kg.bw |
26.6 |
33 |
0.20 |
0.001 |
|
DM intake, g/day (0-150 days) |
||||
|
WS-SPV |
135 |
186 |
1.75 |
0.001 |
|
BR |
424 |
0 |
2.75 |
0.001 |
|
CRM-RB |
0 |
475 |
2.75 |
0.001 |
|
Total |
559 |
661 |
4.9 |
0.001 |
|
CP |
68.6 |
85.2 |
0.70 |
0.001 |
|
g/kg.bw |
30.1 |
33.9 |
0.13 |
0.001 |
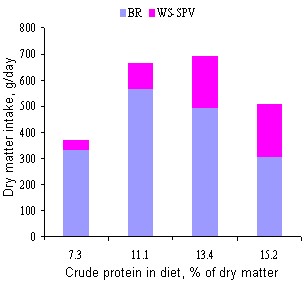
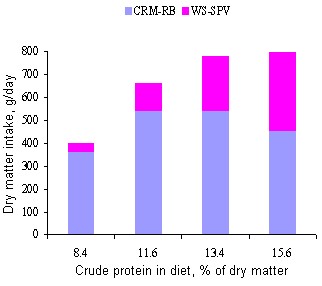
There were significant interactions among treatments for intake of the forages and the total DM intake (Figures 1, 2 and 3).
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Figure 2. Proportion of feed intake and crude protein intake of broken rice alone and water spinach plus sweet potato vine (0-150 days) |
Figure 3. Proportion of feed intake and crude protein intake of cassava root meal mixture rice bran and water spinach plus sweet potato vine(0-150 days) |
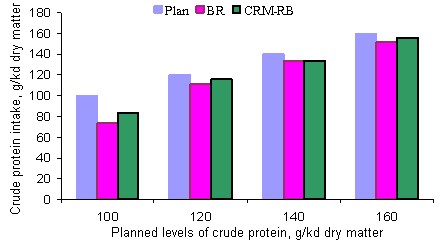
Recorded intakes of crude protein were lower than the planned levels, especially at the lowest level (Table 3).
On the CRM-RB diet the total DM intake increased with increase in protein content of the diet up to 134 g crude protein/kg diet DM and remained at the same level at the highest concentration of crude protein (Table 4). On the BR diet the maximum DM intake was also reached with a protein level of 134 g/kg DM, but decreased significantly at the highest crude protein level. The intake of forages increased with crude protein of the diet on the CRM-RB treatment; in contrast, on the BR diet, intake of the forages showed no increase between 134 and 152g crude protein per kg of diet DM.
|
Table 3. Actual intakes of crude protein compared with the planned level (g crude protein/kg DM) according to the two energy sources |
||
|
Plan |
BR |
CRM-RB |
|
100 |
73.5 |
83.5 |
|
120 |
111 |
116 |
|
140 |
134 |
134 |
|
160 |
152 |
156 |
|
Table 4. Mean values for DM intake of pigs fed basal diets of broken rice or cassava root meal plus rice bran with different levels of protein provided by a 50:50 mixture of sweet potato vines and water spinach |
||||||||
|
|
CP10 |
CP12 |
CP14 |
CP16 |
SEM |
Prob |
||
|
DM intake, g/day ( 0-50 days) |
||||||||
|
WS-SPV |
30 |
80 |
143 |
199 |
|
|
||
|
BR |
191 |
177 |
131 |
89 |
|
|
||
|
CRM-RB |
210 |
189 |
141 |
101 |
|
|
||
|
Total |
431 |
446 |
415 |
389 |
6.65 |
0.001 |
||
|
CP |
37.7 |
50.5 |
54.8 |
56.2 |
1.08 |
0.001 |
||
|
g/kg.bw |
37 |
36.2 |
34 |
32.7 |
0.35 |
0.001 |
||
|
DM intake, g/day ( 50-100 days) |
||||||||
|
WS-SPV |
36 |
112 |
230 |
281 |
|
|
||
|
BR |
156 |
264 |
211 |
142 |
|
|
||
|
CRM-RB |
169 |
248 |
230 |
172 |
|
|
||
|
Total |
361 |
624 |
671 |
595 |
6.45 |
0.001 |
||
|
CP |
29.2 |
74.0 |
92.4 |
93.8 |
0.92 |
0.001 |
||
|
g/kg.bw |
26.5 |
34.2 |
36.1 |
33.8 |
0.23 |
0.001 |
||
|
DM intake, g/day ( 100-150 days) |
||||||||
|
WS-SPV |
44 |
117 |
233 |
316 |
|
|
||
|
BR |
169 |
354 |
347 |
236 |
|
|
||
|
CRM-RB |
188 |
339 |
387 |
352 |
|
|
||
|
Total |
401 |
810 |
967 |
904 |
12.2 |
0.001 |
||
|
CP |
32.7 |
86.4 |
127.6 |
139.9 |
1.82 |
0.001 |
||
|
g/kg.bw |
25.8 |
29.9 |
31.7 |
31.8 |
0.27 |
0.001 |
||
|
DM intake, g/day ( 0-150 days) |
||||||||
|
WS-SPV |
38 |
110 |
220 |
275 |
|
|
||
|
BR |
165 |
283 |
247 |
152 |
|
|
||
|
CRM-RB |
181 |
271 |
272 |
225 |
|
|
||
|
Total |
384 |
664 |
739 |
652 |
6.94 |
0.001 |
||
|
CP |
31.5 |
75.2 |
99.2 |
101.4 |
1.41 |
0.001 |
||
|
g/kg.bw |
27.6 |
33 |
34.4 |
33 |
0.18 |
0.001 |
||
Growth rate and feed conversion
The mean live weights of the pigs at 150-days intervals during the experiment are shown in Table 5.
|
Table 5. Mean values of live weights at 150 days intervals |
||||
|
Live weight |
Planned level of crude protein, % in DM |
|||
|
10 |
12 |
14 |
16 |
|
| Broken rice diets | ||||
|
Initial |
10.9 |
10.9 |
10.9 |
10.9 |
|
50 days |
14.1 |
18.0 |
17.3 |
16.5 |
|
100 days |
16.6 |
25.5 |
26.0 |
23.3 |
|
150 days |
18.5 |
34.6 |
37.4 |
33.8 |
|
Cassava root meal and rice bran diets |
||||
|
Initial |
10.2 |
12.0 |
11.9 |
12.0 |
|
50 days |
12.6 |
17.8 |
18.1 |
17.9 |
|
100 days |
13.7 |
23.9 |
26.1 |
26.8 |
|
150 days |
16.7 |
30.4 |
36.7 |
39.3 |
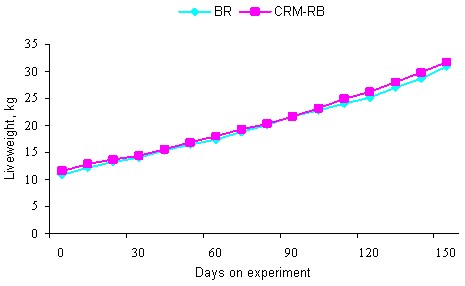
There were no differences in growth rate between the CRM-RB and BR diets at any stage of the experiment (Table 6 and Figure 4).
|
Table 6. Mean values for live weight gain of pigs fed basal diets of broken rice (BR) or cassava root meal plus rice bran CRM-RB) |
||||
|
LWG, g/day |
BR |
CRM-RB |
SEM |
Prob |
|
0-50 days |
103 |
.94.8 |
9.71 |
0.55 |
|
50-100 days |
130 |
121 |
15.5 |
0.71 |
|
100-150days |
161 |
167 |
23.1 |
0.87 |
|
0-150days |
126 |
128 |
14.8 |
0.93 |
|
|
|
Figure 4. Growth curves of the pigs according to the sources of energy |
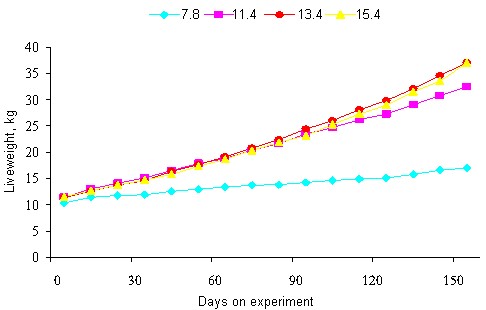
As expected there were differences in growth rate due to protein level at all stages of the experiment (Table 7; Figure 5).
|
Table 7. Mean values for live weight gain of difference protein pigs fed basal diets of broken rice or cassava root meal plus rice bran with different levels of protein provided by a 50:50 mixture of sweet potato vines and water spinach |
||||||
| LWG, g/day | CP10 | CP12 | CP14 | CP16 | SEM | Prob |
|
0-50 days |
54a |
119b |
119bc |
105bd |
14.3 |
0.012 |
|
50-100 days |
42a |
141b |
169bc |
150bd |
22.9 |
0.004 |
|
100-150days |
60a |
156b |
220bc |
220bd |
34.0 |
0.010 |
|
0-150days |
49a |
137b |
167bc |
155bd |
20.9 |
0.004 |
|
ab Means within main effects within rows without common letter are different at P<0.5 |
||||||
|
|
|
Figure 5. Growth curves of the pigs according to the planned levels of crude protein |
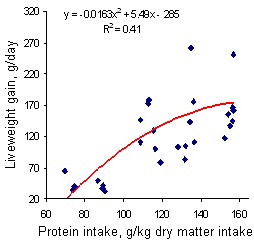
There were no interactions between sources of energy and levels of protein. Growth rates increased with time on the experiment (Tables 6 and 7). On the basis of the growth curves (Figure 5) the optimum crude protein level would appear to be about 14% in diet DM. The curvilinear relationship between live weight gain and crude protein concentration (Figure 6) also indicates little improvement in growth rate when the crude protein exceeded 14% in the diet DM.
|
|
|
|
Feed conversion was better on the BR diets than on the CRM-RB diets (Table 8).
|
Table 8. Mean values for feed conversion of pigs fed basal diets of broken rice (BR) or cassava root meal plus rice bran CRM-RB) |
||||
|
FCR, kg/kg of body weight |
BR |
CRM-RB |
SEM |
Prob |
|
0-50 days |
4.40 |
6.11 |
0.44 |
0.012 |
|
50-100 days |
4.89 |
9.06 |
0.79 |
0.002 |
|
100-150days |
5.74 |
5.78 |
0.45 |
0.95 |
|
0-150days |
5.33 |
6.49 |
0.23 |
0.002 |
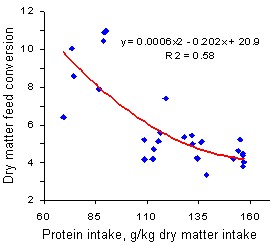
It improved as the protein concentration in the diet increased, in all stages of the experiment (Table 9).
|
Table 9. Mean values for feed conversion ratio of difference protein pigs fed basal diets of broken rice or cassava root meal plus rice bran with different levels of protein provided by a 50:50 mixture of sweet potato vines and water spinach |
||||||
| FCR, kg/kg of body weight | CP10 | CP12 | CP14 | CP16 | SEM | Prob |
|
0-50 days |
9.35a |
4.11b |
3.67bc |
3.90bd |
0.64 |
0.001 |
|
50-100 days |
14.60a |
4.88b |
4.44bc |
3.97bd |
1.17 |
0.001 |
|
100-150days |
8.68a |
5.34b |
4.86bc |
4.18bd |
0.66 |
0.001 |
|
0-150days |
9.46a |
5.09b |
4.73bc |
4.36bd |
0.34 |
0.001 |
The relationship between protein concentration in the diet and feed conversion was curvilinear, indicating there was little improvement in conversion when the crude protein exceeded about 140 g/kg diet DM (Figure 7).
|
|
|
|
Discussion
Diet composition
The DM (16.0%) and crude protein (16.6% in DM) of the sweet potato vines were similar to the values reported by Brown and Chavalimu (1985) (18.1% DM and 17.2% crude protein in the DM). Similar values were reported by Dominguez (1992). The DM and crude protein values for the water spinach (8.9 and 28.8%) differed slightly from those reported by Chhay Ty and Preston (2006b) (DM 11.2 % and crude protein 25.6 %) but were similar to results of Bruemmer and Roe (1979) (8.0 % DM and 29.0% crude protein) and Le Thi Men et al (2000) (crude protein DM o f 28%). The crude protein values of the broken rice, cassava root meal and rice bran were similar to literature reports (Göhl 1971).
Feed intake
The higher DM intake for the diets containing CRM-RB may have been a response of the pigs to the lower energy density (higher fibre content) of this energy source compared with broken rice which contains no fiber. A similar difference was reported by Chiv Phiny et al (2007) comparing cassava root meal and rice bran diets with broken rice and sugar palm syrup. The absolute values for DM intake in our study for the CRM-RB diets were lower than in the experiment of Chiv Phiny et al (2007) because the initial weights in our study were lower (11kg compared with 20kg). There is no obvious explanation for the decrease in DM intake in the BR diet when the protein level was increased from 13.4 to 15.2% in the DM, since this depression was not observed for the CRM-RB diet. On both basal diets the major increase in intake when the crude protein was raised from 7-8% in DM to 11% almost certainly represented a response to an improved balance of protein to energy in the diets.
Growth rates and feed conversion
There appear to be few reports on the effect of protein levels on growth of young pigs given diets in which the major part of the protein was derived from vegetative sources. Nguyen Thi Hoa Ly et al, (2003) compared crude protein levels from 12 to 18% in the DM of diets for pigs (initial weight 20kg) give diets based on rice bran and maize with the protein derived from increasing proportions of sweet potato leaf meal and fish meal. There were no significant differences in the growth rates among protein levels and the authors concluded that the economically optimum level was 14% crude protein in the diet DM for the growth phase from 20 to 50kg. Gonzalez et al (2003) used a design in which sweet potato vines were given free choice and the protein level of the diet was varied by changes in the concentrate supplement in which the range of crude protein was from 13.2 to 25.1% derived mainly from soybean meal. Best results were with the supplement containing 17% crude protein with an overall crude protein in the diet of 17.3% in DM. This level is much higher that the optimum in our study which was with about 14% crude protein in the DM. Prak kea et al (2003) reported a liner increase in growth rates in pigs fed water spinach, broken rice and palm oil when the level of fish meal was raised from 0 to 6% partially replacing the water spinach which decreased from 50 to 29% of the diet, the overall content of crude protein falling slightly from 16.8 to 15.4% in DM.
The
implication of inferior protein quality in sweet potato vines and water spinach
is supported by the finding that when these feeds were major components of the
diet of growing pigs there were improvements in growth rate from supplementation
with lysine in the case of sweet potato vines (Le Van An 2004) and with
methionine in the case of water spinach (Ly et al 2002). Similarly, Du
Thanh Hang et al (2007) recorded significant improvements in growth rate to
methionine supplementation in pigs fed ensiled cassava roots and cassava root
meal when the protein supplement was mainly as fresh cassava leaves.
Conclusions
-
The optimum crude protein concentration for young growing pigs, given diets with low protein sources of energy (mixture of cassava root meal and rice bran or broken rice) and with the protein mainly from high protein forages (water spinach and sweet potato vines), was 14% in the DM.
-
Growth rates were similar for basal diets derived from a mixture of cassava root meal and rice bran, or broken rice; however, feed conversion was better on the broken rice diets.
Acknowledgements
This research thesis was carried out at the ecological farm of the Centre for Livestock and Agriculture Development (CelAgrid) in Cambodia during the period 150days from July 02, 2006 and to December 02, 2006.
The authors would like to express my sincere gratitude to the MEKARN Project with the support from the Swedish International Development Authority (Sida) and Swedish Agency for Research and Cooperation (SAREC) to make this study possible.
Thanks are due to Mr. Chhy Ty for help in analysis the samples in the laboratory and to all staff of CelAgrid, especially Mr. Narum, Pearun, Savy and students of Kampong Cham National school of Agriculture for their assistance during the entire experiment for taking care of the feeding and management of the pigs.
References
AOAC 1990 Official Methods of Analysis: Association of Official Analytical Chemists. 15th edition (K Helrick editor) Arlington pp 1230
Brown D L and Chavalimu E 1985 Effects of ensiling or drying on five forage species in western Kenya: Zea mays (maze stover) Pennisetum purpureum (Pakistan Napier grass) Pennisetum sp. (bana grass) Ipomea batatas (sweet potato vines) and Cajanus cajan (pigeon pea leaves). Animal Feed Science and Technology 13 1-6
Bruemmer J H and Roe B 1979 Protein extraction from water spinach (Ipomoea aquatica ). Proceedings of. Florida Station Horticultural Society 92: 140-143
Chiv Phiny, Ogle B, Preston T R and Khieu Borin 2008
Growth performance of pigs fed water spinach or water spinach
mixed with mulberry leaves, as protein sources in basal diets of
cassava root meal plus rice bran or sugar palm syrup plus broken
rice.
Chhay Ty and Preston T R 2006a Effect of water spinach and fresh cassava leaves on growth performance of pigs fed a basal diet of broken rice. Workshop-seminar "Forages for Pigs and Rabbits" MEKARN-CelAgrid, Phnom Penh, Cambodia, 22-24 August 2006. Article #5 Retrieved April 5, 2007, from http://www.mekarn.org/proprf/chha1.htm
Chhay Ty and Preston T R 2006b Effect of different ratios of water spinach and fresh cassava leaves on growth of pigs fed basal diets of broken rice or mixture of rice bran and cassava root meal. Workshop-seminar "Forages for Pigs and Rabbits" MEKARN-CelAgrid, Phnom Penh, Cambodia, 22-24 August 2006. Article #6 Retrieved April 5, 2007, from http://www.mekarn.org/proprf/chha2.htm
Dahniya M T 1981 Effects of leaf harvests and detopping on the yield of leaves and roots of cassava and sweet potato. In: Terry -E R; Oduro-K A and Caveness F (Editors). International Society for Tropical Root Crops, Ibadan (Nigeria). Africa Branch. Tropical root crops: research strategies for the 1980s. Plantes-racines tropicales : strategies de recherches pour les annees 1980. Ottawa (Canada). IDRC. p. 137-142
Dominguez P L 1992 Feeding of sweet potato in monogastrics. In: Roots, tubers, plantains and bananas in animal feeding (Editors: David Machin and Solveig Nyvold). Animal Production and Health paper No 95, FAO: Rome 1992. pp. 217-23. http://www.fao.org/ag/aga/agap/frg/AHPP95/95-217.pdf
Du Thanh Hang, Linh N Q, Preston T R , Everts H and Beynen A C 2007 Effect of supplementary dl-methionine in pig diets with cassava leaves as a major protein source. PhD thesis, Utrecht University
Duyet Hoang Nghia 2003 The effect of sweet-potato stem levels in the diet on productivity of Mong Cai sows. Science and Technology Journal of Agriculture and Rural Development 6:. 707
Duyet Hoang Nghia, Nguyen Dinh Son, Nguyen Van An and Truong Thi Thuan 2004Effect of high dietary levels of sweet potato leaves on the reproductive performance of pure and crossbred Mong Cai sows; Livestock Research for Rural Development (15) 6 Retrieved May 2, 2004, from http://www.cipav.org.co/lrrd/lrrd15/6/duye156.htm
Eusebio J A 1980 Pig production in the tropics. ITA Series, Longman, Hong Kong
González C, Díaz Ivonne, Vecchionacce H and Ly J 2003 Performance traits of pigs fed sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas L.) foliage ad libitum and graded levels of protein. Livestock Research for Rural Development 15 (9). http://www.cipav.org.co/lrrd/lrrd15/9/gonz159.htm
Göhl B 1971 Tropical feeds. FAO. Animal Production and Health Series, Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nation, Rome, 529 pp
Göhl B 1981 Tropical Feeds. FAO Animal Production and Health Series. No 12 and Revised electronic version at: http://www.fao.org/ag/AGA/AGAP/FRG/afris/default.htm
Hoang Vu Tuyen, Mai Thach Hoanh, Pham Xuan Liem, Vu Dan Thanh and Nguyen The Yen 1993 Preliminary results on breeding for sweet potato as animal feed. Science and Technology Journal of Agriculture and Rural Development, 8:. 306
Ishida H, Suzrno H, Sugiyama N, Innami S, Tadokoro T and Meakawa A 2000 Nutritive value on chemical components of leaves stalks and stems of sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas Poir). Food Chemistry 68: 359-367
Kean Sophea and Preston T R 2001 Comparison of biodigester effluent and urea as fertilizer for water spinach vegetable. Livestock Research for Rural Development (13) 6: http://www.cipav.org.co/lrrd/lrrd13/6/kean136.htm
Khieu Borin, Preston T R and Lindberg J E 1996 Juice production from the sugar palm tree (Borassus flabellifer) in Cambodia and the performance of growing pigs fed sugar palm juice. (MSc thesis in Sustainable Tropical Animal System, Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences, Uppsala). PP1–11
Le Thi Men 1999 Evaluation of water spinach (Ipomoea aquatica) for Baxuyen and Large White sows and fattening crossbred pigs. M.Sc. Thesis. Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences, Department of Animal Utrition and Management,Uppsala
Le Thi Men and Bui Hong Van 1993 Evaluation of diets based on simulated sugarcane juice and water spinach (Ipomoea aquatica) for breeding sows. In Sustainable Livestock Production on Local Feed Resources. Ho Chi Minh City Vietnam 1994
Le Thi Men, Ogle B and Vo Van Son 1999 Evaluation of water spinach (Ipomoea aquatica) for crossbred fattening pigs. Master in Science Thesis. Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences. Uppsala pp 71
Le Thi Men, Ogle B and Vo Van Son 2000 Evaluation of water spinach as a protein source for Baxuyen and Large white sows. Department of Animal Science, College of Agriculture, Cantho University, Vietnam. * Swedent University of Agriculture Science, Department of Animal Nutrient and Management, PO Box 7024, 750 07 Uppsala, Sweden. MSc.Thesis, Swedish University of Agriculture Science, Department of Animal Nutrient and Management, Uppsala 1999, Sweden.
Le Thi Men, Son V V, Manh L H, Khang N T K, Hao T P and Takada R 2000 Evaluation of Water Spinach or Coconut Meal Diet for Fattening Pigs in Tan Phu Thanh Village. Proceeding of the 2001 annual workshop of JIRCAS Mekong Delta Project. 132-139
Le Van An 2004 Sweet potato leaves for growing pigs: Biomass yield, digestion and nutritive value. Doctor's dissertation. ISSN 1401-6249, ISBN 91-576-6750-0 http://diss-epsilon.slu.se/archive/00000639/01/Agraria470.pdf
Le Van An, Hong T T T, Lindberg J E 2004 Ileal and total tract digestibility in growing pigs fed cassava root meal diets with inclusion of fresh, dry and ensiled sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas L. (Lam.)) leaves. Animal Feed Science and Technology 114: 127-139
Le Van An, Lindberg B E F, Lindberg J E 2003 Effect of harvesting interval and defoliation on yield and chemical composition of leaves, stems and tubers of sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas L (Lam.)) plant parts. Field Crops Research 82, 49–58
Ly J, Hean Pheap, Keo Sath and Poksomkol 2002 The effect of DL-methionine supplementation on digestibility and performance traits of growing pigs fed broken rice and water spinach (Ipomonea a quatica).Livestock Research for Rural Development 14(5) http://www.cipav.org.co/lrrd/lrrd14/5/ly145b.htm
MINITAB 2000 Minitab Reference Manual release 13.31
Nguyen Thi Hoa Ly, Nguyen Thi
Loc, Du Thanh Hang and Truong Thi Thuan 2003 Effect of
dietary protein level on the performance of growing pigs under village
conditions in
Prak Kea, Preston, T R and Ly J 2003 Feed intake, digestibility and N retention of a diet of water spinach supplemented with palm oil and / or broken rice and dried fish for growing pigs. Livestock Research for Rural Development (15) 8 Retrieved, from http://www.cipav.org.co/lrrd/lrrd15/8/kea158.htm
Rozemuller M A 1998 >From pig rearing to stock marketing. Rice milling, a broad spectrum of entrepreneurial activities. Center for Advance Study Occasional Paper Series No. 1. Phnom Penh pp 51
Undersander D, Mertens D R and Thiex N 1993 Forage analysis procedures National Forage Testing Association. Omaha pp: 154
Woolfe J A 1992 Sweet potato: an untapped food resource. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 643 pp