 |
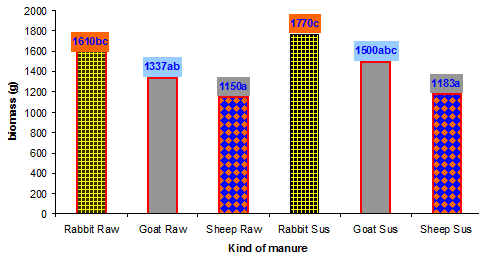
| Figure 1. Worm biomass in different manure sources |
|
MEKARN Conference 2010 |
The experiments were carried out at Goat and Rabbit research Center with 18 beddings of earthworm with 0,5m2 were randomly allocated to 6 treatments with 3*2 factorial arrangements of different manure types that was dry and suspension and raising methods. The manure of goat, sheep and rabbit were prepared 2 weeks before start the experiments. Manure mixed with water before fed to worm with different ratio 5:5 for goat and sheep manure and 7:3 for rabbit manure. The each bedding contained 0.5kg of worm. Worm biomass of rabbit manure is the highest in both raw and suspension at 1610 g, 1770 g respectively, continuously goat manure beds at 1336,7g, 1500g, and the lowest sheep manure beds at 1150 g, 1183,3 g, respectively. Density per grams of worm in raw manure beds is higher trend than suspension manure beds. The different kinds of manure and raw manure or suspension manure do not affect the quantity of worm cast and Chemical composition of worm. The economic efficiency in using suspension manure is higher than using raw manure.
Keyword: Worm, Bedding, Manure, Biomass, Goat, Sheep, Rabbit
 |
| Figure 1. Worm biomass in different manure sources |