|
Back to Content
|
MEKARN Conference 2010
Live
stock production, climate change and resource depletion
|
|
Evaluation of ensiling capacity of Gac shell (Momordica
cochinchinensis Spreng) to be used in chicken and pig feeding
Nguyen Thi Tuyet Le, Le Viet Phuong and Bui Quang Tuan
Abstra
The aim of this study was to
evaluate
effects on fermentation
characteristics and nutritive value of Gac
shells with different additives. Gac shells were treated with 2% mollasses, 3%
and 5% cassava residue, 3 % and 5% maize bran and 10% taro leaves and sterms. Samples will be collected to determine the nutritive value 0, 7, 14, 21,
30 and 60 days of ensiling. Besides, the physical characteristics of the silages
such as color, presence of fungus and smell were evaluated.
Fresh Gac shells showed the low content in dry matter (10,59 % ±0,93) and solube
sugar (0,35% in DM). After 60 days of ensiling,
the quality of silages was
acceptable in terms of odour and appearance
in almost treatment formulas,
with
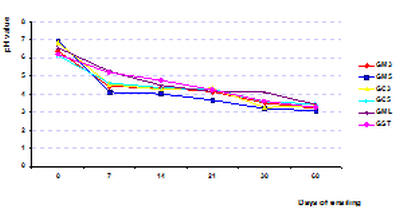
pH
in the range of
3.08-3.62
(Figure 1). The lowest pH value was in the treatment with 5% maize bran and 10%
Taro. Lactic acid concentration
reached 5.09-
6.26
% in dry matter (DM)
after 60 days
(Figure 2).
With the increasing ensiling time, dry matter
content increased and crude protein decreased in all treatments, but the changes
were not significant.
It was concluded that good quality silage
was obtained by ensiling the Gac shells with maize 5% or 10% taro leaves and
stems.
 |
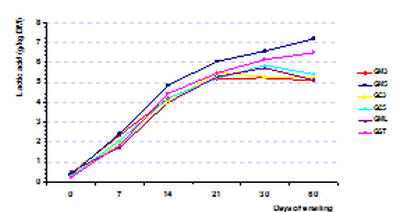 |
Figure 1: Effect of ensiling period and additives
on pH value change
Formula: GM3 is Gac shell + 3% maize;
GM5 is
Gac shell + 5% maize;
GC3 is
Gac shell + 3% cassava residue;
GC5 is
Gac shell + 5% cassava residue;
GML is
Gac shell + 2% molasses;
GST is
Gac shell + 10% taro. |
Figure 2: Effect of ensiling period and
additives on lactic acid content
Formula: GM3 is Gac shell + 3% maize;
GM5 is
Gac shell + 5% maize;
GC3 is
Gac shell + 3% cassava residue;
GC5 is
Gac shell + 5% cassava residue;
GML is
Gac shell + 2% molasses;
GST is
Gac shell + 10% taro. |
Keyword:
Gac shells, nutrition composition, ensilage

