Effect of urea and potassium nitrate on growth
performance of goats fed a basal diet of molasses supplemented with paper
mulberry (Broussonetia papyrifera moraceaae) or Muntingia calabura
foliages
Phonevilay Silivong, T R Preston* and Ngo Van Man
**
Souphanouvong
University, Lao PDR
silipvl@yahoo.co.th
*Finca
Ecologica, TOSOLY, UTA (Colombia)
AA#48, Socorro, Santander,
Colombia
**Department
of Animal Physiology and Biochemistry, Nong Lam University, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
The objective of the present study was to compare the effect of potassium nitrate
or urea on the growth of goats given a basal diet of molasses, supplemented with
foliages of Muntingia or Paper mulberry. The experiment was arranged as
a 2*2 factorial with sixteen local goats (initial average body live-weight
of 13.8 kg and 5-6 months of age) housed in individual cages to give 4 replicates of each treatment. The
factors were: iso-nitrogenous source of NPN (6.0% potassium nitrate or 1.83%
urea) and source of foliage (Paper mulberry or Muntingia) given at 3% of LW (DM
basis). Diluted molasses (Brix value 40) was provided ad libitum. The experiment
lasted 114 days. The goats were adapted to the pens and feeds for 14 days before
starting the experiment. The feeds were offered twice per day at 7:00h and
16:00h.
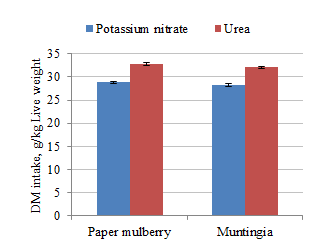
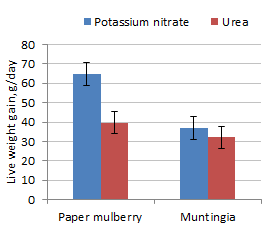
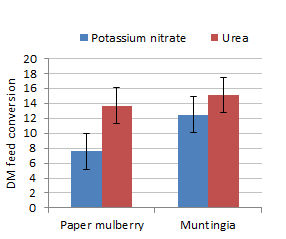
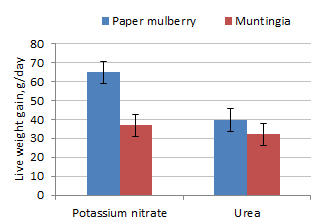
Feed intake was reduced but rate of live weight gain and DM feed conversion were
improved when potassium nitrate replaced urea as the NPN source (Figures 1 to
3). DM feed intake was the same but live weight gain was higher with Paper
mulberry rather than Muntingia (Figure 4).
 |
 |
| Figure 1. Effect of potassium nitrate compared with urea
on DM intake of goats fed molasses and either Paper mulberry
or Muntingia foliages |
Figure 2. Effect of potassium nitrate compared with urea
on live weight gain of goats fed molasses and either Paper mulberry
or Muntingia foliages |
 |
 |
| Figure 3. Effect of potassium nitrate compared with urea
on DM feed conversion of goats fed molasses and either Paper
mulberry or Muntingia foliages |
Figure 4. Effect of Paper mulberry or Muntingia foliages
on live weight gain of goats fed molasses and either potassium
nitrate or urea as source of NPN |
Key words: Feed intake, feed conversion, NPN



