 |
| Brassica juncea L |
|
Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Livestock and Soils |
A biotest with Brassia juncea L .vegetable as a test plant was used to evaluate chicken manure composted with native microorganism (NM), Bio-plant product and fresh water.
 |
| Brassica juncea L |
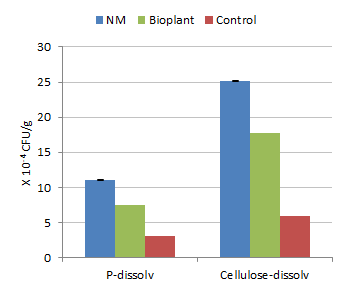
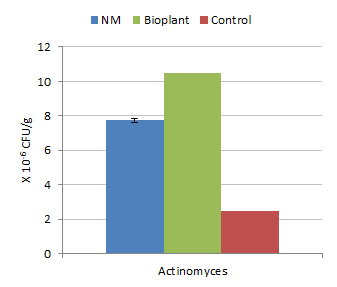
The mixture of native microorganisms (NM) was easy to make, was stable and low cost in comparison with the commercial Bio-plant product. The populations of micro-organisms were much higher in compost inoculated with both " NM" and " Bio-plant" compared with the control (Figures 1-3). The yield of Brassica juncea increased curvilinearly with level of application of the " NM" compost with the peak occurring at 30 tonnes/ha of compost (Figure 4).
Keywords: Organic farming, fertilizer, soil fertility
 |
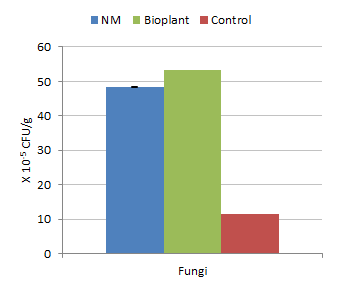 |
| Figure 1. Effect of inoculation with " native" micro-organisms on microbial populations | Figure 2. Effect of inoculation with " native" micro-organisms on fungi population |
 |
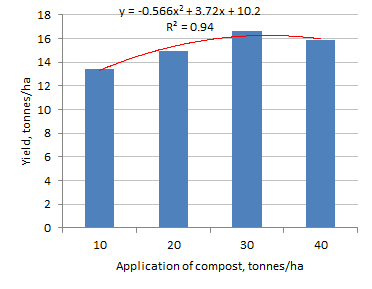 |
| Figure 2. Effect of inoculation with " native" micro-organisms on Actinomyces population | Figure 3. Effect of level of "NM": compost on yield of Brassia juncea |