Effect of Taro (Colocasia esculenta) leaf silage as
replacement for fish meal on feed intake and growth performance of
crossbred pigs
Pheng Buntha, Khieu Borin, T R Preston* and B Ogle**
Center for Livestock and Agriculture
Development
buntha@celagrid.org
*Finca Ecológica, TOSOLY,
Socorro Colombia
**SwedishUniversity of
Agricultural Sciences, Department of Animal Nutrition &
Management,
PO Box7024, 75007,Uppsala,
Sweden
Abstract
Eighteen crossbred (Large White x Local) male pigs with initial
body weight of 20.9± 0.29 kg were allocated randomly into 3
treatments replicated 6 times, with one pig in each pen. The
treatments were ensiled leaves of taro (Colocasia esculenta)
replacing 0 (FM), 50 (FM-TS) or 100 (TS) % of the protein from fish
meal in a basal diet of sugar palm syrup and rice
bran.
Total dry matter feed intake was lower in TS than in FM and
FM-TS (P<0.01), also when expressed on a live weight basis
(37.8, 41.9 and 33.1 g/kg for FM, FM-TS and TS, respectively)
(P<0.01). Average daily gain was highest for FM-TS (278g),
followed by FM (226g) and TS (119g) (P<0.05). Dry matter feed
conversion and cost of feed per kg gain were highest for TS (8.79
kg/kg gain and 2.24 US$/ kg gain, respectively) and lowest for
FM-TS (4.69 kg/kg gain and 1.09 US$/kg gain, respectively)
(P>0.05). Daily gains and feed conversion were only around 50%
of the genetic potential of the pigs for these traits. Further
research is needed to identify the true constraints to pig growth
when protein from ensiled taro leaves is a major component of the
diet.
Key words: Feed conversion ratio, growth, silage, sugar
palm syrup,
Introduction
It is common practice for farmers in rural areas of Cambodia to keep a few local or crossbred pigs in a scavenging system with supplementation of locally available resources, such as rice bran, broken rice, kitchen waste, banana stems, water spinach and other water plants. The live weight gain is low, probably because of the poor quality of the feed, parasite infection and other diseases. In contrast, in the commercial farms the diets are usually based on soybean, cereals and fishmeal. However, this strategy is not appropriate for smallholder farmers because of the high costs of conventional feed ingredients. The proteins in the leaves of many soil and water plant, being composed mostly of enzymes necessary for the growth of plant tissue, have an amino acid balance that resembles the "ideal" protein (Preston 2006). They should therefore be suitable to replace the fish meal and soybean meal used in commercial balanced feeds.
According to Ogle (2006), the constraints in many leaves are the anti-nutritional factors, such as cyanogenic glycosides, trypsin inhibitors, mimosine, goitrogens, oxalic acid, tannins and saponins. Linkages between the protein and fibre can result in decreased digestibility (Jørgensen et al 1996; Kass et al 1980; Shayo and Uden 1999). From studies on the nutritive value of tropical leaves for pigs, Leterme et al (2005) concluded that tropical tree leaves offer a variable amount of proteins that are well balanced in essential amino acids but not well digested by pigs.
Taro is a tropical food crop with high potential because of the high yield of the roots (or corms) and foliage. The leaves are rich in protein and easy to ensile, which has been shown to reduce markedly the concentrations of calcium oxalate (Pheng Bunta et al 2007), which appears to be a limiting factor in consumption of the fresh leaves according to Tiep et al (2006). In the research by Pheng Bunta et al (2007), it was shown that taro leaf silage could replace up to 70-75% of the fish meal protein, with higher feed intakes and N retention than with 100% of the protein from fish meal or from taro leaf silage.
The present study was designed to evaluate taro leaf silage in a
pig growth trial in order to make an economic assessment of its
value relative to fish meal as the main protein source in the diet.
In this trial rice bran was included at 20% of the diet, because it
was observed that the pigs were reluctant to consume a diet
composed only of syrup from sugar palm (Borassus
flabellifer) and fish meal, perhaps because of the absence of
fibre in the diet and a possible deficiency of essential long chain
fatty acids.
Materials and methods
Location and Climate
The study was carried out from December 2006 to March 2007, at the Centre for Livestock and Agriculture Development (CelAgrid) located in Kandal village, Rolous commune, Kandal Stung district, Kandal Province, Cambodia. The climate is tropical monsoonal, with two seasons: a dry season (November-April) and a rainy season (May-October).
Experimental design
Eighteen (Large White x Local) crossbred male pigs with initial body weight of 20.9± 0.29 kg were allocated randomly into 3 treatments, replicated 6 times, with one pig in each pen. The sources of energy were sugar palm syrup and rice bran. The pigs were assigned to treatments in a randomized complete block design (RCBD), with the blocks being the initial live weight (Table 1).
|
Table 1. Experimental layout for the growth performance trial |
|||||
|
Block I |
Block II |
Block III |
Block IV |
Block V |
Block VI |
|
FM |
TS |
FM-TS |
TS |
TS |
FM-TS |
|
TS |
FM-TS |
FM |
FM |
FM-TS |
FM |
|
FM-TS |
FM |
TS |
FM-TS |
FM |
TS |
The experimental treatments were:
FM : Fish meal + palm syrup + rice bran
FM-TS : Taro leaf silage + fish meal + palm syrup + rice bran
TS : Taro leaf silage + palm syrup + rice bran
The protein levels in diets FM-TS and TS were increased relative to diet FM to adjust for the observed lower digestibility of the taro leaf protein (Pheng Buntha et al 2007).
Diets and feeding
The collection and ensiling of the taro leaves and the sources of the palm syrup and fish meal were the same as described by Pheng Buntha et al (2007). Rice bran was purchased from a local rice mill. The pigs were fed ad libitum 3 times per day. All ingredients were mixed together before feeding (see Table 2). Fresh water was available at all times from nipple drinkers. The duration of the experiment was 3 months.
|
Table 2. Ingredient and chemical composition of the experimental diets |
||||||||
|
Ingredients |
|
Diets, % DM basis |
||||||
|
|
Ensiled taro leaves |
Palm syrup |
Rice bran |
Fish meal |
FM |
FM-TS |
TS |
|
|
Taro silage |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
- |
20.2 |
45.0 |
|
Palm Syrup |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
51.5 |
43.6 |
33.5 |
|
Rice bran |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
20.0 |
20.0 |
20.0 |
|
Fish meal |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
27.0 |
14.7 |
- |
|
Salt |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
0.5 |
0.5 |
0.5 |
|
Minerals |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
0.5 |
0.5 |
0.5 |
|
Premix |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
0.5 |
0.5 |
0.5 |
|
Total |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
100.0 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
|
Composition |
|
Calculated from analysis of the ingredients |
||||||
|
DM, % |
18.3 |
53 |
88 |
92 |
|
71 |
59 |
45 |
|
CP in DM, % |
25.9 |
0.24 |
12.0 |
35.6 |
|
12.0 |
12.9 |
14.1 |
|
Calcium oxalate, % in DM |
0.11 |
- |
- |
- |
|
- |
0.22 |
0.50 |
|
Feed cost (US$/kg fresh) |
0.074 |
0.245 |
0.143 |
0.493 |
|
0.29 |
0.18 |
0.12 |
Measurements and data collection
Feed offered and feed residues were recorded daily. The animals
were weighed in the morning before feeding at the beginning and the
end of the experiment and at 10 day intervals. Samples of feed
offered and residues were analysed for DM and N every 10
days.
The measurements taken were as below:
-
Growth rate (g/head/day)
-
Daily feed intake (kg/head/day)
-
Feed conversion ratio (kg feed/kg weight gain)
-
Feed cost (USD/kg weight gain)
Chemical analysis
Feed ingredients were analyzed for DM by microwave radiation (Undersander et al 1993). Total N contents of feeds and residues were determined by the Kjeldahl procedure as outlined by AOAC (1990).
Statistical analysis
The data (feed intake, weight gain and feed conversion) were
analyzed according to the analysis of variance technique using the
general linear model (GLM) procedure in the software of MINITAB
(release 13.31). The sources of variation were treatments, blocks
and error.
Results and discussion
Feed intake
The highest DM intake was recorded for treatment FM-TS (Table 3) and lowest for TS. The reason why the TS pigs were unable to consume the same amount of DM as those on FM-TS may have been the more voluminous nature (bulkiness) of this diet, while on treatment FM it appeared that the problem was the poor acceptability of the mixed ingredients. According to Kyriazakis and Emmans (1995) and Whittemore et al (2002), feed intake in pigs offered high-bulk feeds is restricted due to physiological constraints for the animal. Bulkiness is said to be due to the swelling of hydrated fibre and the final volume depends on fibre composition and structure (Bach Knudsen 2001). Leterme et al (2005) showed that intakes of Xanthosoma leaves by sows were twice as high when these were fed dry compared with the fresh state, but that the water-holding capacity (WHC) was the same for both. They considered that WHC alone could not explain the effects of bulkiness. Chhay Ty et al (2007) reported similar findings to Leterme et al (2005) in that pigs fed ground sun-dried leaves of taro (Colocasia esculenta) consumed more DM than when fed ensiled leaves. More research is needed in order to elucidate the factors determining the intake of taro leaves.
The actual amounts of protein as a percentage of DM that were consumed corresponded approximately to the planned proportions of crude protein in the diet DM, therefore the concentration of dietary protein in the different diets would not appear to have been a factor influencing feed intake.
|
Table 3. Feed intake, live weight changes and feed conversion of pigs fed ensiled taro leaves as replacement for fishmeal |
|||||
|
|
FM* |
FM-TS* |
TS* |
SEM |
P |
|
Live weight, kg |
|
|
|||
|
Initial |
21.0 |
20.8 |
21.0 |
0.29 |
0.92 |
|
Final |
39.2ab |
45.4b |
31.0a |
3.44 |
0.042 |
|
Live weight gain, g/day |
226ab |
278b |
119a |
36.1 |
0.03 |
|
Feed intake, g/day |
|
|
|
|
|
|
DM |
1080b |
1254b |
818a |
80 |
0.006 |
|
Crude protein |
122 |
154 |
113 |
10 |
0.056 |
|
DM / LW, g/kg |
37.8b |
41.9c |
33.1a |
1.32 |
0.003 |
|
CP / DM, g/kg |
111c |
123b |
137a |
1.10 |
0.001 |
|
Conversion |
|||||
|
DM |
5.28 |
4.69 |
8.79 |
1.35 |
0.114 |
|
Crude protein |
0.598b |
0.573b |
1.21a |
0.18 |
0.047 |
|
Cost of feed, US$/kg |
0.408 |
0.305 |
0.267 |
|
|
|
Feed cost /kg gain, US$ |
1.80 |
1.09 |
2.24 |
|
|
|
* See
Footnotes, figure 1 |
|||||
Live weight gain and feed conversion
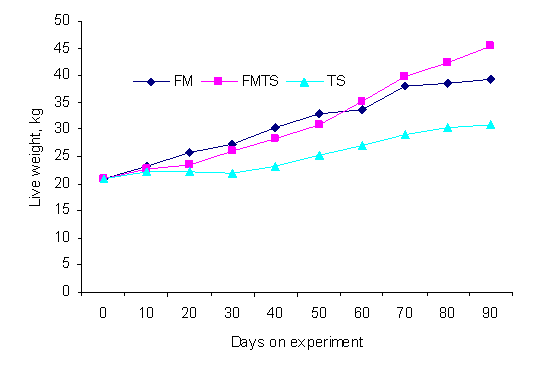
The average growth curves for the different treatments (Figure 1) indicate a long period of adaptation on the 100% taro leaf silage diet (TS). There was a shorter period of adaptation on the 50:50 fish meal: taro leaf silage diet (FM-TS) and a suggestion that towards the end of the trial period the pigs on this treatment were growing considerably faster than on the other two treatments.
|
|
|
Figure 1. Changes in live weight with age in pigs fed
sugar palm syrup and rice bran, with protein supplements of fish
meal (FM), taro leaf silage (TS) or a mixture of the two (FM-TS)
|
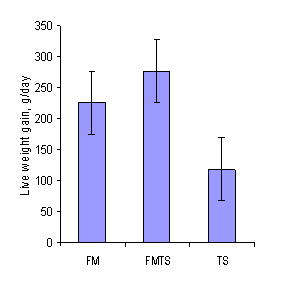
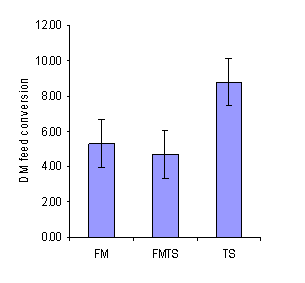
The analysis of the data for final live weight and daily live weight gain paralleled that for DM intake, with the best performance on the FM-TS diet (Table 3; Figure 2). DM feed conversion appeared (P=0.11) to be worse on the TS diet (Table 3; Figure 3).
The growth rates even on the best diet (FM-TS) (278 g/day) were much less than was reported by Rodriguez et al (2006) (524 g/day) for pigs over the same live weight range and fed diets based on sugar cane juice with equal quantities of the protein provided by soybean meal and fresh leaves of New Cocoyam (Xanthosoma sagittifolium). The growth rate on this diet was similar to what was recorded in pigs fed a diet where all the protein was provided by soybean meal (519 g/day). The difference in growth rate on fresh Xanthosoma leaves (Rodriguez et al., 2006a) as protein source and on ensiled Colocasia leaves in the present study was mirrored in the differences in N retention (9.7 and 7.5 g/day for 30 and 60% replacement of soybean meal by Xanthosoma leaves in Rodriguez et al (2006b); and 4.58 g/day for diets with 50% of the protein from ensiled taro leaves (Pheng Buntha et al 2007). There is no apparent explanation for these differences, unless the leaves of taro (Colocasia esculenta) contain as yet unidentified anti-nutritional factors or that the ensiling process results in loss of protein quality (ie; by fermentation of part of the protein to non-protein-nitrogen (Oshima and McDonald 1978)).
Feed costs were lowest for the FM-TS diet, indicating that a
mixture of fish meal and taro leaf silage can be the most
economical for small-holder farmers.
|
|
|
|
|
Figure 2. Mean values (with SE) for live weight gain for
pigs fed sugar palm syrup and rice bran with protein supplements
from fish meal (FM) or taro leaf silage (TS) or a mixture of the
two (FM-TS) |
Figure 3. Mean values (with SE) for DM feed conversion
for pigs fed sugar palm syrup and rice bran with protein
supplements from fish meal (FM) or taro leaf silage (TS) or a
mixture of the two (FM-TS) |
Conclusions
-
The growth performance of pigs fed sugar palm syrup and rice bran was better when fish meal and ensiled taro leaves provided equal proportions of supplementary protein than when fish meal or ensiled taro leaves were the only supplements.
-
However, on the best treatment the growth rate and feed conversion were only some 50% of the genetic potential of the pigs for these traits.
-
Further research is needed to identify the true constraints to pig growth when protein from ensiled taro leaves is a major component of the diet.
Acknowledgments
The present experiment is part of a study on
ensiled taro (Colocasia esculenta) leaves in diet of local
crossbred pigs in Cambodia, supported by the MEKARN project
financed by Sida-SAREC. The authors express their gratitude to all
the personal of the CelAgrid Ecological Farm, for help with the
experiment. This paper forms part of the MSc thesis (MEKARN-SLU,
Uppsala, May 2007), of the senior author.
References
AOAC 1990. Official Methods of Analysis. Association of
Official Analytical Chemists. 15th edition (K Helrick, editor).
Arlington pp 1230
Bach Knudsen KE 2001. The nutritional significance of
dietary fibre analysis. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol.90: 3-20.
http://cat.inist.fr/?aModele=afficheN&cpsidt=1002927
Jørgensen H, Zhao X, Eggum B O and Zhao X Q 1996.
The influence of dietary fiber and environmental temperature on the
development of the gastrointestinal tract, digestibility, degree of
fermentation in the hind-gut and energy metabolism in pigs.
Brit. J. of Nutr. 75: 365-378. http://cat.inist.fr/?aModele=afficheN&cpsidt=3032927
Kass M L, Van Soest P J, Pond W G, Lewis B and McDowell R E
1980. Utilization of dietary fiber from alfalfa by growing
swine. I. Apparent digestibility of diet components in specific
segments of the gastrointestinal tract. J. of Anim.
Sci. 50: 175-181.
Kyriazakis I and Emmans G 1995. The voluntary food intake
of pigs given feeds based on wheat bran, dried citrus pulp and
grass meal, in relation to measurements of food bulk. Br. J.
Nutr. 73: 191-207.
http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/cabi/bjn/1995/00000073/00000002/art00007
Leterme P, Angela M Londono, Fernando Estrada, Wolfgang B S
and Andre B 2005. Chemical composition, nutritive value and
voluntary intake of tropical tree forage and cocoyam in pigs. J.
Sci. Food Agric. 85: 1725-1732.
www.bsas.org.uk/Publications/Animal_Science/2006/Volume_82_Part_2/175/pdf
Ogle B 2006. Forage for pigs: nutritional, physiological
and practical implication. Workshop-seminar "Forages for Pigs and
Rabbits" MEKARN-CelAgrid, Phnom Penh, Cambodia, 22-24 August, 2006.
Article # 15. Retrieved February 8, 107, from
http://www.mekarn.org/proprf/ogle.htm
Oshima M and McDonald P 1978. A review of the changes in nitrogenous compounds of herbage during ensilage. J. Sci. Food Agric.; 29: 497-505
Preston T R 2006. Forages as protein sources for
pigs in the tropics. Workshop-seminar "Forages for Pigs and
Rabbits" MEKARN-CelAgrid, Phnom Penh, Cambodia, 22-24 August, 2006.
Article # 15. Retrieved February 8, 107,
from http://www.mekarn.org/proprf/preston.htm
Shayo C and Uden P 1999. Nutritional uniformity of
crude protein fractions in some tropical browse plants estimated by
two in vitro methods. Anim Feed Sci Technol
78:141-151.
Rodríguez L, Lopez D J, Preston T R and Peters K
2006a. New
Cocoyam (Xanthosoma sagittifolium) leaves as partial
replacement for soya bean meal in sugar cane juice diets for
growing pigs. Workshop-seminar "Forages for Pigs and Rabbits"
MEKARN-CelAgrid, Phnom Penh, Cambodia, 22-24 August, 2006. Article
# 15. Retrieved February 8, 107, from http://www.cipav.org.co/lrrd/lrrd18/7/rodr18091.htm
Rodríguez L, Peniche I and Preston T R
2006b.Digestibility and nitrogen balance in growing pigs fed a
diet of sugar cane juice and fresh leaves of New Cocoyam
(Xanthosoma sagittifolium) as partial or complete
replacement for soybean protein. Workshop-seminar "Forages for Pigs
and Rabbits" MEKARN-CelAgrid, Phnom Penh, Cambodia, 22-24 August,
2006. Article # 15. Retrieved February#MEKARN
MSc 2001-2003 8, 107, from http://www.mekarn.org/proprf/rodr2
.htm
Tiep P S, Nguyen Van Luc, Trinh Quang Tuyen, Nguyen Manh
Hung, Tran Van Tu 2006. Study on the
use of Alocasiamacrorrhiza(roots and leaves) in diets
for crossbred growing pigs under mountainous village conditions in
northern Vietnam. Workshop-seminar "Forages for Pigs and
Rabbits"
MEKARN-CelAgrid, Phnom Penh, Cambodia, 22-24 August, 2006. Article
# 11. Retrieved February 8, 107, from http://www.mekarn.org/proprf/tiep
.htm
Undersander D, Mertens D R and Thiex N
1993.Forage analysis procedures. National Forage Testing
Association. Omaha, pp 154
Whittemore E, Kyriazakis I, Tolkamp B and Emmans G 2002.
The short-term feeding behavior of growing pigs fed foods differing
in bulk content. Physiol. Beh.76: 131-141.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&list_uids=12175596&dopt=Citation