|
Table 1. Layout of the experiment (S is seed; P stem cuttings) |
||||||
|
Level of effluent N, kg/ha |
||||||
|
Block |
Replicate |
200 |
0 |
100 |
150 |
50 |
|
1
|
1 |
S |
P |
S |
P |
S |
|
1 |
P |
S |
P |
S |
P |
|
|
2 |
2 |
P |
P |
S |
S |
S |
|
2 |
S |
S |
P |
P |
P |
|
Procedure
Land preparation
PVC baskets, lined with polyethylene (capacity about 50 litre, area 0.16 m²) were filled with soil to a depth of 20 cm. The soil contained 0.097% of N and had a pH of 7.46.
Planting the water spinach
The dry-land water spinach species was chosen for both seed and stem planting, which was done on August 3, 2003. The seeds were kept in water at ambient temperature for 12 hours before planting in rows across the basket at a spacing of 3-4 cm and at 1-2 cm depth. The distance between rows was 10cm, and the overall seeding density was 62.5g/m2. The stems for planting were each 5 cm long and were taken from a section starting 4-5 cm from the main root. They were planted at spacing of 5cm x 5cm, equivalent to an average of 30 plants per basket (equal to 200 plants/m²) (Photos 1 and 2).
 |
 |
| Photo 1: Planting the stem cuttings | Photo 2: Fertilising the water spinach after 14 days |
Fertilizing
The biodigester effluent was applied every 4 days for a total of 6 times during the growing period. It contained 410 mg N/litre, thus the total amounts used were 0, 1.95, 3.9, 5.85 and 7.8 kg in each basket over the 24 day period, divided in 6 equal applications. The effluent was from a biodigester charged with cow manure managed with a 20 day retention time and a charging rate of 4 kg solids per 1 m³ of liquid volume (Bui Phan Thu Hang 2003).
Irrigation
The plants were irrigated twice a day (morning and afternoon) at the rate of 3 to 4 litres/m²). On rainy days no additional water was applied.
Measurements
Plant height was measured every 4 days before applying the
effluent. The measurement was done on a random number of plants (10 plants/basket). The water spinach was harvested at 24
days after planting. All plants were separated into stem and leaf, and after
weighing the two components, samples were analysed immediately
to determine dry matter by microwave radiation (Undersander et al
1993), N (AOAC 1990) and water extractable DM and N (Ly and Preston
1997).
Statistical analysis
The data were analysed by ANOVA using the General Linear
Model (GML) software of Minitab (Version Release 13.2). Sources of
variation were: planting materials (S, P), effluent N level, the
interaction of plant material*level N, blocks and error.
Results and discussion
Water spinach growth
The height of the water spinach increased linearly with level of effluent up to 150 kg N/ha (Table 2 and Figure 1) with no further increase for 200 kg N/ha. The water spinach planted from seed had faster growth in the first 4 days (P=0.023) but there was no difference in the rate of growth in height between the two plant materials (Table 3). There were differences between the two blocks in rate of growth in height (P=0.008) with the highest value for block 2, situated close to a wall which perhaps shielded the plants from excessive wind and rain, which occurred at intervals during the experiment.
|
Table 2. Least square means for height (cm) due to effluent level effect |
|||||||
|
N level |
4days |
8days |
12days |
16days |
20days |
24days |
Increase, cm/day |
|
0 |
4.94 |
8.39 |
12.8 |
14.8 |
18.0 |
20.6 |
0.78 |
|
50 |
4.03 |
7.66 |
14.4 |
19.2 |
25.3 |
28.5 |
1.29 |
|
100 |
4.74 |
8.73 |
14.9 |
21.8 |
29.9 |
35.4 |
1.60 |
|
150 |
4.58 |
8.03 |
15.5 |
23.8 |
32.5 |
38.4 |
1.79 |
|
200 |
4.46 |
8.34 |
16.7 |
24.8 |
33.7 |
39.4 |
1.85 |
|
SEM |
0.278 |
0.494 |
0.68 |
0.86 |
1.02 |
1.02 |
0.054 |
|
Prob |
0.270 |
0.634 |
0.032 |
0.001 |
0.001 |
0.001 |
0.001 |
|
Table 3. Least square means for height due to planting material effect |
|||||||
|
|
4days |
8days |
12days |
16days |
20days |
24days |
Increase, cm/day |
|
Stem |
4.21 |
8.00 |
13.2 |
19.6 |
26.9 |
28.8 |
1.452 |
|
Seed |
4.89 |
8.46 |
16.5 |
22.1 |
28.8 |
32.7 |
1.47 |
|
SEM |
0.176 |
0.313 |
0.428 |
0.547 |
0.645 |
0.647 |
0.034 |
|
Prob |
0.023 |
0.325 |
0.000 |
0.009 |
0.069 |
0.567 |
0.72 |
The growth in height of the water spinach was similar to the findings of Ngo Tien Dung (2001) (42 cm with 40 kg N/ha over 28 days) and San Thy and Preston (2001) (47 cm with 140 kg N/ha in 28 days), taking account of the shorter growth period (24 days) in the present experiment.
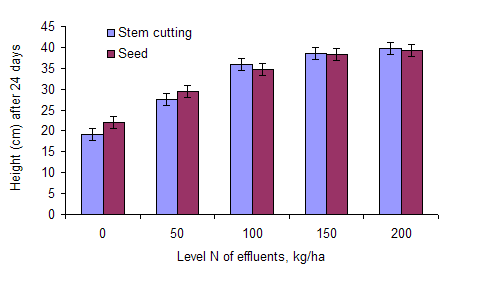
Figure 1. Mean values for height of water spinach after 24 days according
to effluent N levels
and source of planting material
Biomass yield
The hypothesis that biomass yield would be higher by planting from seed was verified by the results (Table 4). Response to effluent N level was curvilinear for planting from seed and linear for planting with stem cuttings (Figure 2). Maximum yield for seed planting (15,000 kg/ha) was lower than was reported in Cambodia (23,600 kg/ha with 140 kg N from effluent) by Kean Sophea and Preston (2001), but higher than was found from application. Differences in soil and climate could be the reason for the differences. There appears to be no information in the literature on yield responses to fertilizer with stem cuttings as plant material.
The proportion of leaf in the fresh biomass was higher for stem planting, presumably because the plants were less mature, but there was no consistent trend for effect of effluent N level (Table 3).
|
Table 4. Least square means for fresh biomass yield and proportion of leaf material according to effluent N level and source of planting material |
||||
|
|
Stem |
Seed |
||
|
Treat |
Yield, kg/ha |
% leaf |
Yield, kg/ha |
% leaf |
|
0 |
2000 |
51.2 |
4219 |
38.8 |
|
50 |
4531 |
45.7 |
7656 |
39.6 |
|
100 |
6094 |
43.2 |
11563 |
36.6 |
|
150 |
7187 |
42.4 |
13500 |
36.8 |
|
200 |
9219 |
43.7 |
15000 |
39.9 |
|
Mean |
5820 |
45.3 |
10380 |
38.3 |
|
Yield: SEM/Prob
plant material effect 403/0.001 |
||||
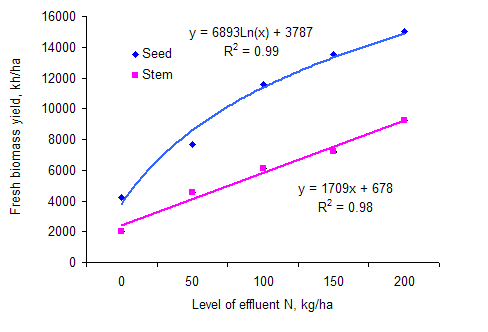
Figure 2: Response in biomass yield to effluent N level with two sources of plant material
Dry matter and Nitrogen content, N recovery of the
water spinach
The DM content of the leaves and stems decreased as effluent fertilizer level was increased; and leaves had higher DM content than stems (Table 5; Figure 3). Nitrogen (and therefore crude protein) in leaves increased with effluent N level as far as 150 kg N/ha, but then leveled off (Figure 4). Crude protein in the stems was much lower than in the leaves, and appeared to decrease with increasing effluent N level, but the trend was not uniform (Figure 4).
|
Table 5. Least square means for DM and N in stems and leaves of water spinach according to level of effluent N in kg/ha |
|||||||
|
|
0 |
50 |
100 |
150 |
200 |
SEM |
Prob. |
|
Dry matter content, % |
|||||||
|
Leaf |
10.2 |
10.3 |
9.42 |
9.20 |
9.37 |
0.194 |
0.007 |
|
Stem |
8.09 |
7.30 |
6.43 |
6.13 |
6.33 |
0.194 |
0.001 |
|
N content in DM, % |
|||||||
|
Leaf |
3.08 |
3.74 |
4.33 |
5.66 |
5.56 |
0.156 |
0.001 |
|
Stem |
2.01 |
1.10 |
1.26 |
1.40 |
1.19 |
0.191 |
0.121 |
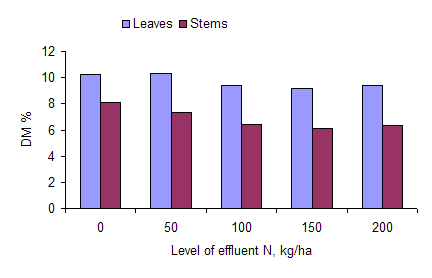
Figure 3: DM content of leaves and stems of water spinach according to level of effluent N
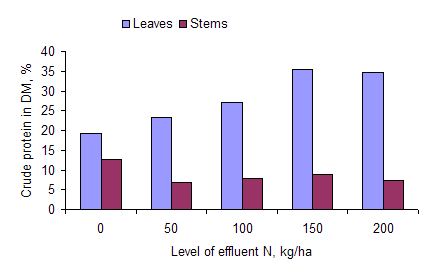
Figure 4: Mean values for content of
crude protein in leaf and stem of water spinach according
to effluent N level
Water extractable DM and N
There was no effect of planting materials, and no interaction between planting materials and N level of effluent on the water extractable DM and N, therefore the data in Table 6 and Figure 5 are from the average of the sources of the planting material.
|
Table 6. Least square means for water extractable DM and N according to N levels of effluent |
||||
|
|
Water extractable DM |
Water extractable N |
||
|
Level N |
Leaves |
Stems |
Leaves |
Stems |
|
0 |
24.6 |
34.8 |
60.8 |
52.9 |
|
50 |
36.8 |
43.3 |
65.1 |
64.4 |
|
100 |
46.3 |
50.3 |
52.6 |
51.3 |
|
150 |
41.9 |
53.4 |
55.4 |
62.2 |
|
200 |
39.6 |
44.6 |
61.4 |
56.3 |

Figure 5. Water extractable DM in leaves and stems according to level of effluent N

Figure 6. Water extractable N in leaves and stems according to level of effluent N
N recovery
The recovery of the N applied in the effluent, calculated as [(N in plant biomass/Total N applied)*100], decreased with increasing levels of application of N in the effluent (Figure 7), and was higher in the water spinach planted from seed. Higher values than these were reported by Kean Sophea and Preston (2001), but they planted the water spinach on raised beds of soil, and obtained higher yields, probably because of better utilization of soil nutrients.

Figure 7. Recovery of N by water spinach fertilized with increasing levels of effluent N
Conclusions
- Fresh biomass yields were higher (15 tonnes/ha) when water spinach was established from seed than from stem cuttings (9.18 tonnes/ha).
- Biomass yields of water spinach increased linearly with effluent N level when planted from stem cuttings and logarithmically when planted from seed.
- The N content of water spinach leaves increased from 3.08 to 5.56% in DM (19.3 to 34.8% crude protein) by application of 200 kg N/ha as biodigester effluent. Stems were much lower in N (1.2 to 2.0% in DM) and this index tended to decrease with increasing application of effluent N.
- Water extractable N tended to be higher in leaves than in stems but the converse was true for the water extractable DM.
- Water extractable DM in leaves and stems increased with level of effluent N up to 100 kg/ha but then declined. Effluent N level had no effect on water extractable N.
Acknowledgements
This experiment was part of the MSc (2003-05), supported by
the MEKARN project financed by sida-SAREC. The author expresses his gratitude to all the
personnel of the Agriculture and Natural Resources faculty of An Giang University, for assistance with the experiment. Grateful thanks
are given to Dr T R Preston, and his colleagues (Dr J Ly, Mr Chhay Ty and Mr
San Thy) for advice and supervision during the conduct of the
present study.
References
AOAC 1990 Official Methods of Analysis. Association of Official Analytical Chemists. 15th edition (K Helrick, editor). Arlington pp 1230
Bui Xuan An, PrestonT R and Dolberg F 1997 The introduction of low-cost polyethylene tube biodigesters on small scale farms in Vietnam. Livestock Research for Rural Development (9) 2: http://www.cipav.org.co/lrrd/lrrd9/2/an92.htm
Bui Phan Thu Hang 2003: Effect of dimensions of plastic biodigester (width:length
ratio) on gas production and composition of effluent; Retrieved,
from MEKARN Mini-projects.
Heifer Project International-Cambodia 2002 Country strategic plan regarding livestock development project with the poor farmer families at the rural communities in Cambodia. Heifer Project International-Cambodia, Phnom Penh
Kean Sophea and Preston T R 2001 Comparison of biodigester effluent and urea as fertilizer for water spinach vegetable. Livestock Research for Rural Development (13)6: http://www.cipav.org.co/lrrd13/6/Kean136.htm.
Ly J and Preston T
R 1997 An approach to the estimation of washing losses in leaves of tropical
trees. Livestock Research for Rural Development (9)3: http://cipav.org.co.lrrd/lrrd9/3/ly931.htm
Ly J and Preston T R 2001 In
vitro estimates of nitrogen digestibility for pigs and
water-soluble nitrogen are correlated in tropical forages feeds.
Livestock Research for Rural Development 13(1): http://cipav.org.co.lrrd/lrrd13/1/ly131.htm
Ngo Tien Dung 2001 Response of water spinach (Ipomoea aquatica) to fertilization with increasing concentrations of the rubber tree latex wash water and biodigester effluent. http://www.mekarn.org/msc2001-03/minipro/dung.htm
Preston T R and Leng R A 1989 The greenhouse
effects and its implications for world agriculture. The need for
environmentally friendly development. Livestock Research for Rural
Development (1).
http://www.cipav.org.co/lrrd/
San Thy and Preston T R 2003
Evaluation of
the effluent from different retention times as fertilizer for
growing water spinach (Ipomoea aquatica).
Undersander D, Mertens D R and Theix N 1993 Forage
analysis procedures. National Forage Testing Association. Omaha pp
154.